How CERT-RMM and NIST Security Controls Help Protect Data Privacy and Enable GDPR Compliance, Part 1: Identifying Personally Identifiable Information
The costs of the steady stream of data breaches and attacks on sensitive and confidential data continue to rise. Organizations are responding by making data protection a critical component of their leadership and governance strategies. The European Union's recent General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) adds layers of complexity to protecting the data of individuals in the EU and European Economic Area. Organizations are struggling to understand GDPR's requirements, much less become compliant. In this series of blog posts, I'll describe how to use the CERT Resilience Management Model (CERT-RMM) to approach GDPR compliance and, more fundamentally, data privacy.
The European Commission defines personal data to be "any information relating to an individual, whether it relates to his or her private, professional or public life." Under GDPR, which went into effect on May 25, 2018, businesses are required not only to comply with requirements but to demonstrate their compliance.
At its core, GDPR is about risk, in this case data privacy and security. Dealing with risk is not new to the many organizations that have used CERT-RMM's resilience-focused approach to establishing threat and incident management programs. However, in the face of GDPR's requirements to address data privacy risk--and EU data subjects already filing access requests with U.S. organizations--most data owners don't know what to do. Fortunately, just as CERT-RMM can drive resilience activities at the threat and incident management level, it can do the same at the enterprise level for GDPR compliance.
Adapting CERT-RMM for Data Privacy
Data owners can use the GDPR compliance and privacy scenario to address the requests for EU subject data they are currently receiving. However, with no established baseline for normal GDPR compliance, data owners can only respond in an unsustainable, ad hoc manner. I believe organizations can use CERT-RMM to create process improvement efforts to comply with the GDPR regulation. My goal is to adapt CERT-RMM for data privacy by creating a model view of CERT-RMM relationships that drive resilience activities at the enterprise, engineering, operations, and process management levels.
CERT-RMM provides a model of an organization that is resilient to disruption. The model has 26 process areas that each include a mixture of specific and general goals and practices. Twelve of the process areas drive the resilience management of data subjects' information privacy. They establish and use requirements for protecting and sustaining data subjects' information and privacy. The CERT-RMM process areas establish PII as a key element in service delivery.
| CERT-RMM Process Area | Operational Resilience Management Area |
|---|---|
| Asset Definition and Management (ADM) | Engineering |
| Controls Management (CTRL) | Engineering |
| Requirements Resilience Management (RRM) | Engineering |
| Service Continuity (SC) | Engineering |
| Compliance Management (COMP) | Enterprise Management |
| Organizational Training and Awareness (OTA) | Enterprise Management |
| Risk Management (RISK) | Enterprise Management |
| Asset Management (AM) | Operations |
| Incident Management and Control (IMC) | Operations |
| External Dependencies Management (EXD) | Operations |
| Vulnerability Access and Resolution (VAR) | Operations |
| Monitoring (MON) | Process Management |
Privacy by Design
GDPR requires data owners to implement "Data protection by design and by default." Organizations will need to design privacy into their policies, procedures, and systems from the inception of organizational services, products, and processes. The CERT-RMM process areas above provide a resilience-based approach to privacy by design, considering the nature, purposes, context, and scope of the processes and their implications.
As with privacy design principles generally, not all 12 process areas will apply in all use cases, and the use of some CERT-RMM process areas can conflict with the use of others. Ultimately the process areas chosen are a cluster of related practices in an area that, when implemented collectively, satisfy a set of goals for making improvement in that area. Choosing which ones to implement depends on the people, information, technology, facilities, and organizational culture.
Using CERT-RMM to Identify Personally Identifiable Information
The first step for an organization improving data privacy and complying with GDPR is to identify what it needs to protect: any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person (data subject), special categories of personal data, the digital systems storing personal data, and the categories of data they hold. Once the organization knows how the data is used and what value it holds, it can decide how to protect it under the organization's Risk Management program.
Organizations can use CERT-RMM to implement an asset and risk management strategy that provides complete visibility of their assets. The following 10 process areas guide organizations through the identification of PII:
| CERT-RMM Process Area | Operational Resilience Management Area |
|---|---|
| Asset Definition and Management (ADM) | Engineering |
| Controls Management (CTRL) | Engineering |
| Requirements Resilience Management (RRM) | Engineering |
| Service Continuity (SC) | Engineering |
| Compliance Management (COMP) | Enterprise Management |
| Organizational Training and Awareness (OTA) | Enterprise Management |
| Risk Management (RISK) | Enterprise Management |
| Asset Management (AM) | Operations |
| External Dependencies Management (EXD) | Operations |
| Monitoring (MON) | Process Management |
The CERT-RMM process areas above can be used to map to the following Articles of GDPR:
- Article 1: Subject-matter and objectives (data protection as a fundamental right)
- Article 2: Material scope (processing of personal data wholly or partly)
- Article 4: Definitions (information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person, or data subject)
- Article 6: Lawfulness of processing (compliance with existing laws)
- Article 8: Conditions applicable to child's consent in relation to information society services (compliance with laws, policies, and regulations of data privacy for children)
- Article 9: Processing of special categories of personal data
- Article 24: Responsibility of the controller (ensure and demonstrate processing follows GDPR)
Figure 1 shows the portion of the model view of CERT-RMM relationships that drive resilience activities specifically about identifying PII.
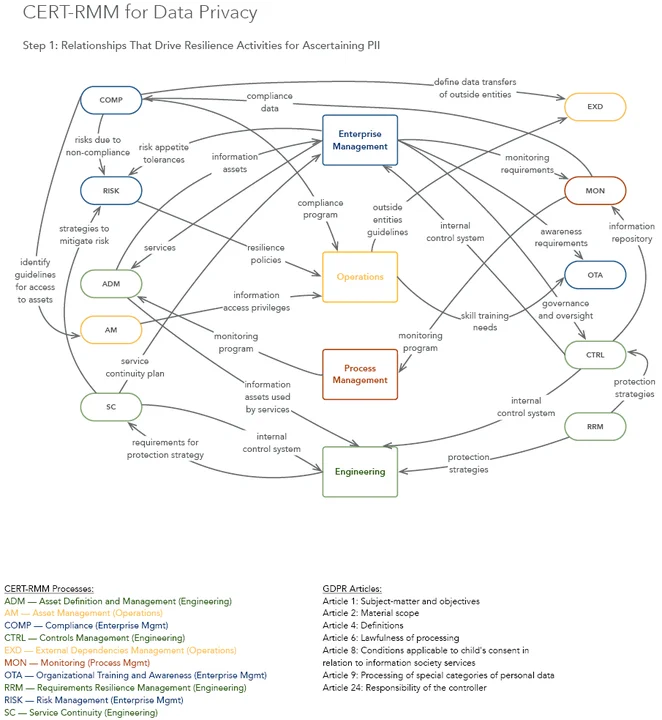
Figure 1: CERT-RMM relationships that drive resilience activities for identifying PII
Data Privacy Is Good Business
With data breaches at an all-time high, the time is now for organizations to identify and protect the privacy of all their data subjects and drive toward compliance to the GDPR. Failure to do so will lead to significant disruption of business. What's more, adhering to a process model, such as CERT-RMM, can ultimately help organizations and businesses attract and retain data subjects. In the case of the GDPR, compliance demonstrates the organization's investments in security, privacy, and usability.
By communicating how they handle data privacy, organizations can build trust with data subjects, differentiate themselves from competitors, and grow in the global marketplace. Organizations must look within and beyond their network to identify and protect all data subjects. We recommend application of CERT-RMM to address the process of data privacy and bridge the GDPR compliance gap.
In the next entry, I'll show how to protect data privacy with CERT-RMM.
More By The Author
More In Insider Threat
PUBLISHED IN
Get updates on our latest work.
Sign up to have the latest post sent to your inbox weekly.
Subscribe Get our RSS feedMore In Insider Threat
Get updates on our latest work.
Each week, our researchers write about the latest in software engineering, cybersecurity and artificial intelligence. Sign up to get the latest post sent to your inbox the day it's published.
Subscribe Get our RSS feed
